Making Texas high schools career-ready
This is a preview of our Texas 2036 newsletter on efforts to prepare a career-ready future workforce. To receive this weekly look at our work, sign up here.
Closing the skills gap starts in TX high schools

While 90% of Texas high school students currently graduate, and 63% of jobs in Texas require some sort of postsecondary education or training:
- As of 2023, 25% of students who had started eighth grade a decade prior had completed a postsecondary credential. That breaks down further to:
- 20% of young men
- 30% of young women
That’s why the Texas Legislature is acting now to equip high school students with the skills and credentials to thrive in a changing economy. We look at the data and what’s next.
How Texas labor markets are changing

Between 2021 to 2031, Texas will see nearly 1.7 million job openings each year, mostly from new jobs and retirements, according to the latest report by Georgetown University.
Of those new jobs, nearly 1 million are expected to require some level of credential.
Help wanted: Middle-skill workers are in demand
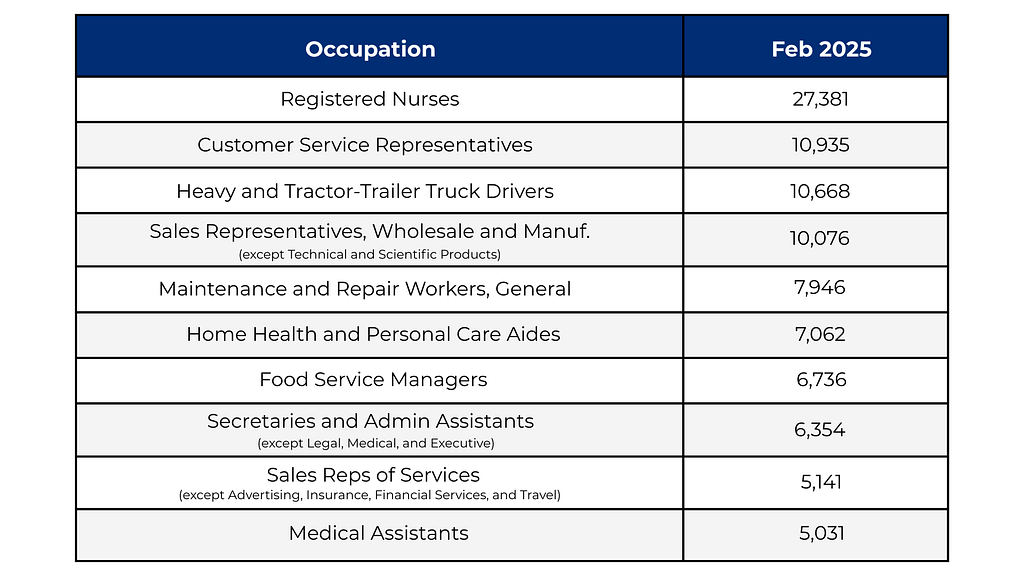 Source: “Top Middle-Skill Occupations by Postings,” Texas Workforce Commission (Texas Labor Market Review, March 2025)
Source: “Top Middle-Skill Occupations by Postings,” Texas Workforce Commission (Texas Labor Market Review, March 2025)
Middle-skill jobs made up around 43% of all job postings in Texas as of February 2025, according to the Texas Workforce Commission. These jobs require more than a high school diploma but less than a bachelor’s degree.
Types of middle-skill jobs include: the skilled trades (i.e. electricians, plumbers and welders), health care, IT and tech support, manufacturing, transportation and public safety.
What does it take to get by in Texas?
According to 2025 data from the Texas Workforce Commission:
- The average Texas family needs $72,561/year to be self-sufficient
- The average individual needs to earn $17.18/hour (varies by county)
* This self-sufficient wage is based on a calculation of the average Texas family as 1.78 adults and 1.68 children.
Lawmakers laid a foundation for student success

Texas has made strides in recent years toward building the workforce of the future through legislative reforms like:
- House Bill 3 (2019) tied public school funding to student outcomes.
- House Bill 8 (2023) did the same for community colleges, rewarding credentials of value.
Together, these reforms create incentives for students to earn valuable credentials before finishing high school.
🗣️ And in his 2025 State of the State address, Gov. Greg Abbott made “life-changing career training” a top priority, highlighting growing momentum to continue to connect education with workforce needs.
From data to impact: Research that shapes policy

Since 2020, Texas 2036 has produced key tools and reports that have shaped both current and past legislative sessions, including:
- Aim Hire Texas Regional Workforce Data (2020)
- Postsecondary Outcomes Exploration Tool (2021)
- Community College Finance Simulator (2022)
- Leveraging the Potential of Community Colleges in Policy and Data-Driven Workforce Development (2023)
- The State of Readiness: Are Texas students prepared for life after high school? (2023)
- Workforce Composition, Trends and Alignment Report (2023)
- The Texas 2036 Difference: Rethinking Community Colleges and the Workforce of the Future (2023)
- Advanced Coursetaking Dashboard (2024)
- Solving for X in Texas (2024)
- Improving Funding Efficiencies for Classroom-to-Career Programs in Texas (2024)
- Pathways to Rural Careers in Texas (2025)
Texas workforce training bills on the table
 Source: Texas Education Agency (Career and Technical Education)
Source: Texas Education Agency (Career and Technical Education)
Right now, the Texas Legislature is advancing key efforts this session to improve career education and workforce readiness for students statewide.
Here’s a closer look at this session’s most prominent career training bill:
📘 HB 120 – Major Career Training Bill
Author: Rep. Keith Bell (R-Forney)
What it does:
- Modernizes Career and Technical Education (CTE) programs to align with industry-recognized credentials
- Expands the Rural Pathways Excellence Partnership (R-PEP) to bring career training to more rural students
- Covers dual credit costs for students in Pathways in Technology Early College High School (P-TECH) schools and R-PEP
- Launches a statewide advising program for career and education planning
📣 Highlight: The Houston Chronicle’s Chris Tomlinson highlighted HB 120 in a recent column. He writes, “As four-year degrees become more expensive and less beneficial, better workforce training in public schools will meet both employer and student needs.” Read more.
🚍 Texas 2036 Research in Action:
Giving Rural Schools and Students a Leg Up

Texas 2036’s “Pathways to Rural Careers in Texas” lays out policy solutions designed to put more rural high school students on the path to success:
- Build on local efforts: Leverages programs like R-PEP already making a difference in rural schools.
- Strengthen career pathways: Expands postsecondary opportunities and workforce credentials to students still in high school.
- Support local economies: Helps students stay and thrive in their hometowns by connecting them to good, family-sustaining jobs.
- Secure Texas’ future: Recognizes that rural talent is essential to the state’s long-term economic prosperity.
💡 The bottom line: Strong rural education-to-career pipelines help ensure Texas stays economically competitive—today and in the future.
📺 On the National Stage: Rural Innovation in South Texas

CBS Evening News recently spotlighted a powerful example of rural collaboration in action: the Rural Schools Innovation Zone (RSIZ).
RSIZ is a first-of-its-kind partnership between five South Texas school districts working together to improve college and career opportunities for students. They also serve as a successful case study for braided funding.
Did you know? Educators from 46 states have come to take a look at RSIZ.
🌟 Why It Matters: RSIZ shows how rural communities can innovate through partnership, offering students greater opportunities without leaving their hometowns.
 Paris Chacon, 17, is the youngest student enrolled in phase three of the nursing program. A sixth-semester student, she graduated from Mission Early College High School on June 9, 2023.
Paris Chacon, 17, is the youngest student enrolled in phase three of the nursing program. A sixth-semester student, she graduated from Mission Early College High School on June 9, 2023.
(Source: The University of Texas at El Paso, College of Nursing)
👀 Other Career Education Bills to Watch:
- HB 2189 (Rep. Donna Howard, D-Austin): Supports partnerships that grow health care-focused CTE and dual credit programs.
- HB 2196/SB 569 (Rep. Bell & Sen. Paul Bettencourt, R-Houston): Allows districts and charter schools to offer high-quality virtual and hybrid career education options.
- HB 2110/SB 1786 (Rep. Gary VanDeaver, R-New Boston & Sen. Brandon Creighton, R-Conroe): Builds on the new community college funding reforms first passed in 2023, including refining credentials of value and improving the data sources that will allow community colleges to tailor their programs to local labor market needs.
- HJR 5/SJR 59 (Rep. Stan Lambert, R-Abilene & Sen. Brian Birdwell, R-Granbury): Establishes an endowment fund for the Texas State Technical College.
Training the next generation of Texas talent

In summary, Texas talent is shaped in high school. That’s why Texas 2036 and legislators have focused on initiatives that can help ensure Texas students graduate ready for successful careers.
✅ Alignment with Industry Needs: Texas CTE programs that match employer demands help students get hired and close skill gaps.
✅ Equitable Access to Quality Education: Rural partnerships help ensure all Texas students can access career opportunities no matter where they live.
✅ Enhanced Career Guidance: High school counseling helps students make informed career choices.
✅ Early Exposure to Technical Careers: Expanding P-TECH and career readiness programs to more high schools gives students early, practical experience in technical fields — preparing them for college or the workforce.
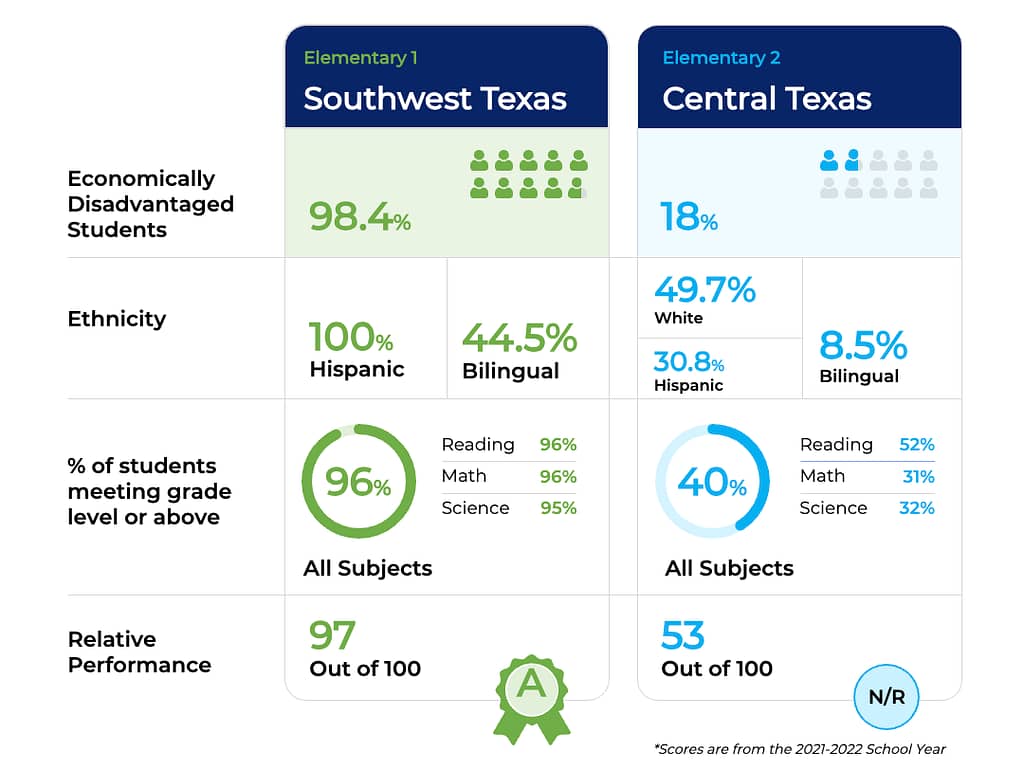
📝 A win on A-F accountability
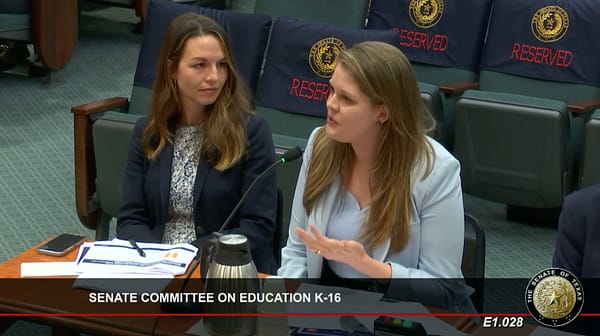 Director of Education and Workforce Mary Lynn Pruneda discusses the Laredo ISD success story in testimony on April 1 before the Senate Committee on Education K-16.
Director of Education and Workforce Mary Lynn Pruneda discusses the Laredo ISD success story in testimony on April 1 before the Senate Committee on Education K-16.
Last week, the 15th Court of Appeals cleared the release of Texas’ 2023 A–F academic accountability ratings—a key tool for tracking student progress in public schools.
📣 Why it matters: As Mary Lynn Pruneda testified, there’s an academic miracle going on at a campus in Laredo ISD. But without publicly available A-F ratings, we wouldn’t know about these success stories happening across the state.
Now, it’s time to release the 2024 performance scores.
Texas 2036 talks workforce issues

📸: President and CEO David Leebron participated in a workforce panel on April 10 hosted by greater:SATX at the San Antonio-Austin Megaregional Collaborative held at Texas State.